Plastic bag waste poses a significant environmental concern, impacting ecosystems and contributing to pollution. Recycling plastic bags is crucial to mitigating this problem and promoting sustainability. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of plastic bag recycling, covering everything from understanding local programs to adopting eco-friendly alternatives.
The increasing prevalence of plastic bags in our daily lives has led to a growing need for effective recycling methods. This guide explores the various aspects of plastic bag recycling, including the different types of plastic bags, recycling programs available, and the best practices for proper disposal. By understanding the complexities and nuances of recycling plastic bags, we can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Introduction to Plastic Bag Recycling

Plastic bags, ubiquitous in modern commerce and daily life, pose a significant environmental challenge. Their widespread use has led to a massive accumulation of waste, creating pollution in ecosystems and hindering natural processes. This accumulation negatively impacts wildlife, waterways, and overall environmental health. Recycling plastic bags is a critical step in mitigating these harmful effects and promoting a more sustainable future.The importance of recycling plastic bags extends beyond the reduction of waste.
It conserves natural resources, minimizes pollution, and reduces the strain on landfills. By recycling plastic bags, we can lessen our dependence on virgin materials, thereby preserving forests and other ecosystems. Recycling these bags also reduces the need for energy-intensive manufacturing processes, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
The Problem of Plastic Bag Waste
Plastic bags, due to their lightweight and durable nature, are easily dispersed into the environment. This results in widespread contamination of natural landscapes, particularly in oceans and waterways. Animals often mistake plastic bags for food, leading to ingestion and subsequent health problems, or entanglement, causing injury or death. The long-term effects of this pollution are still being studied, but the damage to wildlife populations is evident.
The accumulation of plastic bag waste in landfills also contributes to the overall problem of waste management, and poses a risk to groundwater contamination.
Importance of Recycling Plastic Bags
Recycling plastic bags is a crucial aspect of a sustainable waste management strategy. It reduces the demand for virgin plastic production, minimizing the use of fossil fuels and the resulting greenhouse gas emissions. By diverting plastic bags from landfills, we conserve valuable landfill space and prevent the leaching of harmful chemicals into the environment. Recycling efforts also create new economic opportunities by enabling the development of recycling industries and supporting related jobs.
Environmental Benefits of Recycling Plastic Bags
Recycling plastic bags offers numerous environmental advantages. It reduces the need for new plastic production, conserving fossil fuel resources and decreasing carbon emissions. This translates to a smaller ecological footprint. Furthermore, it minimizes the volume of waste ending up in landfills, reducing the risk of pollution and environmental damage. By diverting plastic bags from landfills, recycling efforts contribute to preserving natural habitats and protecting wildlife.
History of Plastic Bag Use and Disposal
The widespread use of plastic bags began in the mid-20th century, coinciding with the rise of consumerism and convenience. Initially, the disposal of plastic bags was often informal, and their environmental impact was largely unrecognized. Over time, the accumulation of plastic bags in the environment became increasingly apparent, leading to growing public awareness and the development of recycling programs.
The history of plastic bag usage and its impact on the environment highlight the urgency of sustainable practices.
Types of Plastic Bags and Recyclability
| Type of Bag | Recyclable? | Notes ||—|—|—|| Grocery Bags | Often, but varies by location | Check local regulations and recycling facilities for specific guidelines. Some grocery stores may have their own recycling programs. || Shopping Bags | Varies greatly | Look for bags made from recyclable materials (often labeled as such). Many retailers use a variety of materials for their bags, which impacts recyclability.
|| Produce Bags | Typically recyclable | Again, check local regulations and recycling programs. Some produce bags are specifically designed for composting or biodegradation. || Other Plastic Bags | Varies | The recyclability of other types of plastic bags (e.g., dry cleaning bags, bread bags) depends on the material used in their production. |
Understanding Plastic Bag Recycling Programs
Plastic bag recycling programs vary significantly across regions, reflecting diverse environmental priorities and infrastructure capabilities. Understanding these variations is crucial for individuals and businesses to effectively participate in recycling efforts. Properly understanding and adhering to local regulations is vital to ensuring the successful recycling of plastic bags.Recycling programs often have specific guidelines about the types of plastic bags accepted, their condition, and the designated collection points.
This complexity necessitates a clear understanding of local requirements.
Common Plastic Bag Recycling Programs
Different municipalities and regions have adopted various approaches to plastic bag recycling. Some programs focus on specific types of plastic bags, while others prioritize the overall collection and processing of plastic materials. This diverse approach reflects the differing priorities and environmental contexts across different locations.
- Many cities and states have implemented programs that accept plastic bags made from certain types of plastics, usually #2 or #4. Examples include HDPE (high-density polyethylene) and LDPE (low-density polyethylene). These materials are often used in grocery and shopping bags.
- Some programs have specific requirements for bag cleanliness and condition, such as avoiding contamination with food waste or other materials. This ensures that the plastic bags are suitable for the recycling process.
- Certain locations may have specific regulations for the disposal of plastic bags, even if they are not part of a formal recycling program. This often involves curbside collection or designated drop-off locations.
Recycling Criteria in Different Regions
Recycling programs often establish criteria for accepting plastic bags. These criteria ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of the recycling process.
- Plastic bag recycling programs may mandate specific types of bags for collection, such as those from grocery stores or specific retailers. This specificity is meant to streamline the sorting and processing procedures.
- Cleanliness is a critical criterion. Contaminated bags with food residue or other materials significantly hinder the recycling process. This often leads to the rejection of these bags.
- Bag size and thickness can influence the program’s ability to effectively recycle them. Programs may have limitations on the size and type of plastic bags they can handle.
Comparison of Recycling Programs Across Countries
Recycling programs for plastic bags vary considerably across different countries, reflecting differing environmental policies and technological capabilities.
- European countries, for instance, often have more comprehensive and well-established plastic bag recycling programs, sometimes with higher standards for material purity. This often reflects a longer history of environmental awareness and investment in recycling infrastructure.
- In North America, the availability and scope of plastic bag recycling programs are more geographically varied. Some states have robust programs, while others have limited or no dedicated recycling initiatives for plastic bags.
- The development and implementation of these programs are often influenced by the specific environmental conditions, economic factors, and societal attitudes in each region. This highlights the importance of adapting recycling programs to local needs and circumstances.
Sorting and Processing Plastic Bags
The sorting and processing of plastic bags are crucial steps in the recycling process. Efficient sorting minimizes contamination and maximizes the quality of the recycled material.
- Plastic bags are typically separated from other recyclables through visual inspection and automated sorting techniques. This process ensures that only plastic bags are processed.
- The next step often involves washing the bags to remove any residual contaminants, such as food particles. This improves the quality of the recycled plastic.
- The cleaned bags are then shredded or processed into smaller pieces, preparing them for further use in manufacturing new products.
Requirements for Plastic Bag Recycling in Municipalities
Municipalities typically have specific guidelines for plastic bag recycling. These guidelines vary based on local regulations and infrastructure.
| Municipality | Plastic Bag Types Accepted | Contamination Restrictions | Collection Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example City A | HDPE, LDPE bags from grocery stores only | No food or other debris | Dedicated drop-off bins at designated locations |
| Example City B | All types of plastic bags, regardless of source | Limited contamination permitted; bags must be clean | Curbside collection |
Methods for Recycling Plastic Bags
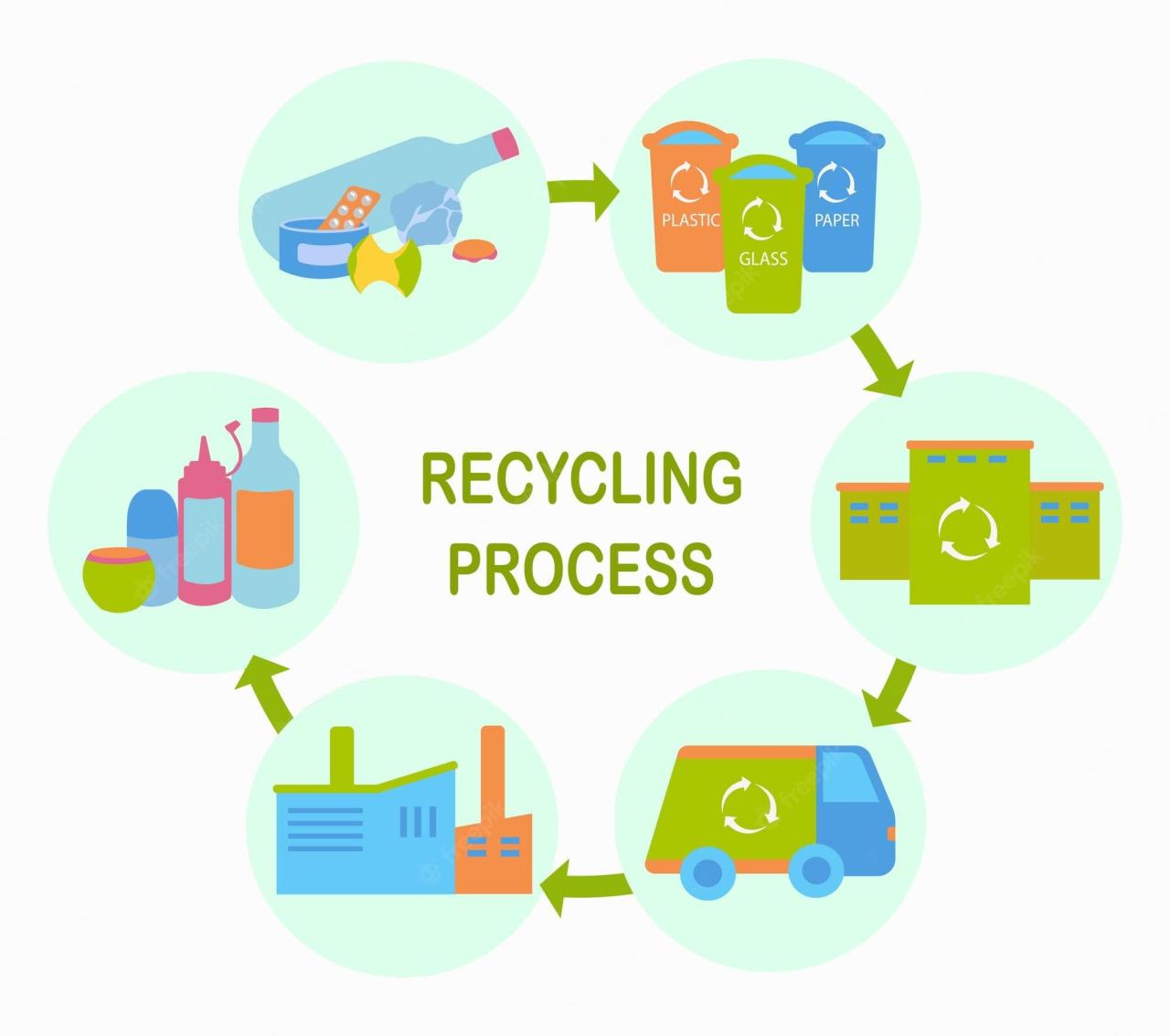
Recycling plastic bags is a crucial step in reducing plastic pollution and conserving resources. Effective collection and sorting methods are essential for successful recycling programs. Proper preparation of plastic bags ensures efficient processing and maximizes the quality of the recycled material.Effective plastic bag recycling hinges on efficient collection and processing methods. This section details the different approaches to recycling plastic bags, from household collection to community-based initiatives.
Understanding these methods is critical for individuals and communities to contribute meaningfully to plastic bag reduction and responsible waste management.
Plastic Bag Collection Methods
Various methods exist for collecting plastic bags for recycling. These methods range from designated drop-off points to curbside collection programs. The best method depends on the specific community and its infrastructure.
- Designated Drop-Off Points: These locations, often found at grocery stores, supermarkets, and community centers, provide a convenient method for residents to deposit their plastic bags. Dedicated bins or containers are typically used to segregate plastic bags from other waste materials.
- Curbside Collection Programs: In many municipalities, plastic bags are collected curbside as part of regular waste collection services. However, these programs often require the plastic bags to be separated from other waste and placed in designated containers or bags.
- Community-Based Initiatives: Local organizations and community groups sometimes organize collection drives and initiatives to collect plastic bags from residents and businesses. These initiatives can be targeted towards specific areas or communities to address localized plastic bag usage.
Plastic Bag Sorting Methods
Efficient sorting of plastic bags is crucial for effective recycling. Different methods are employed to separate plastic bags from other materials. The sorting process helps ensure the purity of the recycled material.
- Manual Sorting: Manual sorting involves human workers meticulously examining and separating plastic bags from other waste materials. This method can be labor-intensive but remains important for smaller-scale recycling programs.
- Automated Sorting: Automated sorting machines use advanced technologies like optical sensors and conveyors to automatically identify and separate plastic bags from other materials. These machines are often more efficient and can process large volumes of plastic bags.
Preparing Plastic Bags for Recycling
Proper preparation of plastic bags before recycling significantly impacts the quality of the recycled material. Minimizing contamination is crucial.
- Empty and Clean: Ensure that the plastic bag is completely empty of any contents. Remove any food residue, labels, or other contaminants that might hinder the recycling process.
- Flatten and Compact: Flatten the plastic bag to minimize its volume and maximize the capacity of the recycling container. Compacting helps to make the sorting and processing more efficient.
- Separate from Other Materials: Always keep plastic bags separate from other types of waste, such as paper, cardboard, glass, or metal. Mixing different materials can hinder the recycling process.
Step-by-Step Guide for Home Recycling
This guide provides a straightforward process for recycling plastic bags at home.
- Collect: Gather all clean plastic bags from your household. Ensure they are empty and free from any contaminants.
- Flatten: Gently flatten the plastic bags to minimize their volume and maximize space in the recycling container.
- Separate: Place the flattened bags into a dedicated recycling bin or bag, ensuring they are separate from other waste materials.
- Dispose: Properly dispose of the plastic bags at a designated recycling center or through your community’s curbside recycling program.
Types of Plastic Bag Recycling Machines
Recycling machines vary in complexity and capacity. The type of machine used depends on the scale of the recycling operation.
- Manual Sorting Tables: Simple tables equipped with manual sorting tools, typically used in smaller-scale recycling facilities.
- Automated Sorting Machines: Sophisticated machines using optical sensors, conveyors, and other technologies for automated sorting.
- Shredding Machines: Machines that shred plastic bags into smaller pieces, facilitating the recycling process and reducing bulk.
Community-Based Recycling Initiatives
Community-based recycling initiatives are often successful in promoting plastic bag recycling.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with local businesses and community groups can help establish dedicated drop-off points and raise awareness.
- Educational Programs: Organizing educational programs to inform residents about proper plastic bag recycling techniques can improve participation.
- Incentives: Offering incentives, such as discounts or rewards, can motivate residents to actively participate in plastic bag recycling.
Tips for Successful Plastic Bag Recycling
These tips will help maximize your success in plastic bag recycling.
- Proper Preparation: Ensure plastic bags are clean, empty, and flattened before disposal.
- Separate from Other Waste: Always keep plastic bags separate from other waste materials.
- Follow Local Guidelines: Adhere to your local community’s plastic bag recycling guidelines and policies.
- Support Community Initiatives: Participate in community-based recycling programs and initiatives.
Comparison of Collection and Sorting Methods
The table below compares different plastic bag collection and sorting methods.
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Designated Drop-Off Points | Dedicated bins at designated locations | Convenient for residents | May not be accessible for all |
| Curbside Collection | Collection as part of regular waste collection | Convenient for residents | Requires separation from other waste |
| Community-Based Initiatives | Organized drives by community groups | Raises awareness and engagement | May be limited in scope |
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Plastic bag recycling, while a valuable environmental initiative, faces challenges due to common misconceptions and errors in practice. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for maximizing recycling success and minimizing the environmental impact of plastic bags. This section details frequent errors, clarifies the reasons behind the non-recyclability of some bags, and addresses widespread misunderstandings.
Common Recycling Errors
Many recycling programs encounter issues due to improper bag handling. Incorrectly sorted bags, contamination, and inadequate preparation can hinder successful recycling processes. For instance, bags often get mixed with other recyclables, such as paper or cardboard, which can render the entire batch unsuitable for processing. This emphasizes the need for meticulous sorting and handling.
Reasons for Non-Recyclability
Not all plastic bags are created equal in terms of recyclability. Different types of plastic polymers, varying thicknesses, and the presence of contaminants often make a bag unsuitable for recycling. Some bags might contain multiple layers of different plastics, rendering them too complex for efficient recycling methods. Additionally, contamination from food residue, grease, or other materials can prevent the bag from being properly processed.
These factors significantly affect the viability of recycling programs.
Misconceptions About Plastic Bag Recycling
Some prevalent misconceptions hinder effective recycling. A common misconception is that all plastic bags are recyclable, which is inaccurate. Another misconception involves the idea that bags can be recycled in any recycling bin. The reality is that many recycling programs have specific requirements for plastic bags, often requiring a distinct type of container or specific bag type.
These misconceptions lead to wasted resources and hinder recycling efforts.
Impact of Incorrect Practices
Improper plastic bag recycling can have several negative consequences. Firstly, it leads to the waste of valuable resources that could have been diverted from landfills. Secondly, it creates unnecessary environmental strain by increasing the volume of non-recyclable materials in waste streams. Thirdly, it may compromise the quality and efficiency of the overall recycling process, impacting the quality of the recovered materials.
Non-Recyclable Plastic Bag Types
Certain types of plastic bags are generally not accepted in standard recycling programs. This includes plastic bags containing food residue or contaminants, heavily soiled or damaged bags, and bags with complex polymer blends. Moreover, some plastic bags are too thin or too thick for standard recycling processes.
Recyclable vs. Non-Recyclable Plastic Bags
| Characteristic | Recyclable Plastic Bags | Non-Recyclable Plastic Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Typically single-layer, common plastic types (e.g., HDPE, LDPE) | Multiple layers, blends of plastics, contaminated, heavily soiled, or damaged |
| Contamination | Clean, free of food residue or other contaminants | Contaminated with food, grease, or other materials |
| Thickness | Appropriate thickness for recycling processes | Extremely thin or excessively thick |
| Examples | Plastic grocery bags (certain types), some shopping bags | Bags with complex mixes, heavily soiled produce bags, some packaging materials |
Improving Plastic Bag Recycling

Encouraging wider participation in plastic bag recycling is crucial for reducing environmental impact and achieving sustainability goals. This necessitates a multifaceted approach involving individuals, businesses, and governmental entities. Effective strategies are essential to transform plastic bag recycling from a niche practice to a widespread and impactful behavior.
Encouraging Public Participation
To foster greater public engagement in plastic bag recycling, clear and consistent communication is paramount. Educational campaigns, utilizing various media platforms, can effectively raise awareness about the benefits of recycling and the proper methods. Incentives, such as discounts or rewards programs, can motivate individuals to actively participate in recycling initiatives. Community-based initiatives, involving workshops, presentations, and volunteer activities, can empower communities to become actively involved in recycling programs.
These community efforts can help to promote awareness, build social norms, and improve overall participation rates.
Government and Business Roles
Government regulations and corporate policies play a vital role in promoting plastic bag recycling. Mandatory recycling programs, including specific guidelines and regulations for businesses, can mandate the collection and processing of plastic bags. Government subsidies and tax incentives for recycling programs can encourage businesses to invest in recycling infrastructure and technologies. Corporate social responsibility initiatives by businesses can motivate them to integrate recycling programs into their operations and encourage consumer participation.
Furthermore, partnerships between governments and businesses can leverage resources and expertise to optimize recycling programs.
Improving Recycling Infrastructure
Optimizing plastic bag recycling infrastructure requires a strategic approach to ensure efficient collection, sorting, and processing. Investing in dedicated collection bins and sorting facilities for plastic bags, strategically located in high-traffic areas, is crucial. Partnering with local waste management companies to enhance the capacity for handling plastic bags is essential. Establishing clear guidelines for the types of plastic bags accepted for recycling can prevent contamination and ensure efficient processing.
Moreover, promoting the use of standardized bag types that are more easily recyclable can streamline the recycling process.
Successful Recycling Campaigns
Several successful plastic bag recycling campaigns have demonstrated the effectiveness of community engagement and targeted interventions. For example, campaigns in certain European cities have successfully increased plastic bag recycling rates by implementing clear labeling of recycling bins, providing clear instructions for consumers, and offering rewards for participation. Successful campaigns have consistently demonstrated the value of public awareness and streamlined processes.
Innovative Recycling Technologies
Exploring innovative recycling technologies can revolutionize the processing of plastic bags. Advanced sorting technologies, using optical sensors or other methods, can effectively separate different types of plastic bags and other materials. Chemical recycling methods can break down plastic bags into their basic components, enabling the production of new materials. These advanced technologies can significantly enhance recycling efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of plastic bags.
Supporting Local Recycling Initiatives
Supporting local recycling initiatives is essential for community-based environmental sustainability. Participating in local clean-up drives, volunteering time at recycling centers, and advocating for improved recycling infrastructure are all ways to contribute. Contacting local government representatives to express support for recycling initiatives can help in securing resources and funding. Promoting recycling programs at community events can foster a sense of collective responsibility.
Summary of Actions
| Action | Individual | Business | Government |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Awareness | Support educational campaigns; use reusable bags | Implement internal recycling programs; educate employees | Launch public awareness campaigns; mandate educational programs |
| Infrastructure Improvement | Use designated recycling bins; properly sort bags | Invest in recycling equipment; partner with recycling centers | Fund infrastructure improvements; establish clear guidelines |
| Policy Support | Advocate for improved recycling policies; participate in public discussions | Support recycling policies; implement sustainability goals | Implement policies encouraging recycling; enforce regulations |
Alternatives to Plastic Bags
Beyond recycling, transitioning to reusable alternatives offers significant environmental and economic advantages. Adopting reusable bags is a crucial step in reducing plastic pollution and promoting sustainability. This approach not only protects the environment but also fosters responsible consumption habits.
Reusable Alternatives to Plastic Bags
A wide variety of reusable alternatives to plastic bags are available, catering to diverse needs and preferences. These alternatives offer practical solutions for carrying groceries, shopping, and other everyday tasks. Reusable bags are designed to be durable and convenient, allowing for multiple uses and reducing the need for single-use plastic.
- Canvas bags:
- Sturdy and durable, canvas bags are crafted from cotton or linen. They are easily washable and maintain their shape well. These bags are a popular choice for their aesthetic appeal and eco-conscious nature.
- String bags:
- Often made of cotton or jute, string bags are lightweight and easily foldable. Their simple design makes them practical for carrying smaller items or light loads. These bags are highly versatile for various purposes.
- Mesh bags:
- Lightweight and breathable, mesh bags are ideal for carrying produce and other items requiring air circulation. Their open weave structure allows for proper ventilation, preventing spoilage.
- Shopping totes:
- Spacious and durable, shopping totes provide ample space for carrying larger quantities of groceries or other items. They are often made from recycled materials and come in various colors and patterns. These bags are highly convenient for bulk shopping and errands.
- Rucksacks or backpacks:
- Large backpacks or rucksacks can be used for carrying a wide range of items, including clothing, books, and groceries. These bags are particularly useful for larger shopping trips and outdoor activities. They are versatile and highly functional.
Environmental Benefits of Reusable Bags
The environmental impact of choosing reusable bags is substantial. By reducing reliance on single-use plastic bags, we significantly lessen our contribution to plastic waste accumulation in landfills and the marine environment. Reusable bags also minimize the demand for new plastic production, conserving natural resources and reducing the associated pollution.
Economic Impact of Reusable Bags
The shift to reusable bags can yield economic benefits for individuals and businesses. Investing in reusable bags represents a long-term cost-effective solution. Reusable bags eliminate the need for frequent plastic bag purchases, resulting in significant cost savings over time. Businesses that embrace reusable bag programs can potentially reduce their environmental footprint and enhance their brand image, attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
Comparison of Plastic Bags and Reusable Bags
| Characteristic | Plastic Bags | Reusable Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | High; contributes to pollution and waste | Low; promotes resource conservation and reduces waste |
| Cost | Low initial cost, but high long-term cost due to repeated purchases | Higher initial cost, but lower long-term cost due to reusability |
| Convenience | Easy to obtain, but single-use and often inconvenient for multiple trips | Requires initial investment, but convenient for multiple trips and offers greater versatility |
Importance of Choosing Eco-Friendly Alternatives
Embracing eco-friendly alternatives like reusable bags is crucial for a sustainable future. The shift from single-use to reusable solutions is a critical step in reducing plastic pollution, protecting ecosystems, and promoting responsible consumption patterns. Making conscious choices about the materials we use directly impacts the environment.
Case Studies of Businesses Transitioning to Reusable Bags
Numerous businesses have successfully transitioned to reusable bag programs. For instance, several grocery stores have implemented initiatives to encourage the use of reusable bags, providing discounts or incentives to customers. This demonstrates that businesses are actively taking steps to reduce plastic waste and enhance their environmental image. Similarly, other retail establishments have adopted reusable bag programs to promote sustainability and customer loyalty.
These examples highlight the potential of businesses to drive significant environmental and economic change by choosing eco-friendly alternatives.
Conclusive Thoughts

In conclusion, recycling plastic bags is a multifaceted process requiring knowledge of local programs, proper sorting methods, and the use of eco-friendly alternatives. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this comprehensive guide, individuals can play a vital role in reducing plastic waste and promoting a more sustainable future. We encourage readers to embrace these practices and inspire others to do the same.