Reducing your carbon footprint is crucial for a sustainable future. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of actionable steps, from simple lifestyle changes to impactful community initiatives. Understanding the various sources of your carbon emissions, such as transportation, energy consumption, and food choices, is the first step toward making a positive impact.
We’ll explore practical methods for reducing your environmental impact, including choosing sustainable transportation options, adopting energy-efficient habits, and making conscious food choices. By understanding the lifecycle of products and embracing sustainable consumption patterns, you can significantly decrease your ecological footprint.
Transportation
Transportation is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing sustainable transportation options is crucial for reducing your personal carbon footprint. By understanding the environmental impact of different modes of transport, we can make informed decisions to minimize our contribution to climate change.Reducing transportation emissions requires a shift towards more sustainable practices. This includes exploring alternative modes of transport, optimizing vehicle usage, and promoting efficient travel habits.
By embracing these strategies, we can significantly lower our carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future.
Alternative Transportation Methods
Various methods exist for reducing your transportation-related carbon footprint. Choosing sustainable alternatives to personal vehicles is a key component of this reduction. Public transport, cycling, and walking are all effective ways to lessen your environmental impact.
- Public Transportation: Utilizing buses, trains, and subways is generally more environmentally friendly than driving a personal vehicle, as the emissions are shared among many passengers. This results in a lower per-passenger emission rate compared to individual car use. For example, a train journey often involves significantly lower emissions than multiple car journeys.
- Cycling: Cycling is an excellent way to reduce emissions, as it generates zero tailpipe emissions. It offers a healthy and eco-friendly alternative for short-to-medium distances. A great example is commuting to work or running errands.
- Walking: Walking is the most sustainable mode of transport, producing zero emissions. It is ideal for short distances and contributes significantly to reducing your overall carbon footprint. Perfect for local trips around your neighborhood or shorter commutes.
Comparing Carbon Emissions of Transport Modes
Understanding the emissions associated with different modes of transport is essential for making informed choices. This comparison highlights the environmental impact of each method.
| Transport Mode | Carbon Emissions (per passenger-kilometer) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Car | High | Convenience, flexibility | High emissions, dependence on fossil fuels |
| Bus | Medium | Cost-effective, large capacity | Limited routes, schedule constraints |
| Train | Low | Long-distance travel, relatively efficient | Limited routes, time constraints |
| Bike | Very Low | Healthy, zero emissions | Suitable for short distances, weather dependent |
| Walking | Zero | Healthy, no emissions, convenient for short distances | Limited distance, time constraints |
The table above provides a comparative overview of carbon emissions per passenger-kilometer for various transport modes.
Reducing Carbon Footprint When Driving
Even when driving, there are ways to mitigate your environmental impact. These steps focus on optimizing your driving habits and vehicle efficiency.
- Improving Fuel Efficiency: Regular maintenance, proper tire pressure, and avoiding aggressive driving can significantly improve fuel efficiency. This leads to a reduction in fuel consumption and consequently, emissions.
- Carpooling: Sharing a ride with others can substantially decrease emissions. Pooling resources to travel to work or other destinations reduces the number of vehicles on the road, minimizing overall emissions.
- Utilizing Public Transport: When possible, consider utilizing public transportation to reduce the number of individual vehicles on the road, thereby minimizing emissions.
- Electric Vehicles: Electric vehicles (EVs) offer a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing your carbon footprint.
Energy Consumption

Reducing energy consumption in households is crucial for mitigating our carbon footprint. Effective strategies in this area can significantly lessen the environmental impact of our daily activities. By adopting energy-efficient practices, we contribute to a more sustainable future.Efficient energy use directly translates to lower carbon emissions. This reduction contributes to a healthier planet and, in the long term, benefits all of us.
Implementing these practices within our homes not only minimizes our environmental impact but also can lead to considerable savings on utility bills.
Strategies for Reducing Household Energy Consumption
Various strategies can be employed to reduce household energy consumption. These range from simple lifestyle adjustments to the selection of energy-efficient appliances. Understanding these strategies empowers individuals to make informed decisions that contribute to a greener future.
- Improving Home Insulation: Proper insulation significantly reduces heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This leads to lower energy requirements for heating and cooling, thereby decreasing overall energy consumption. For example, upgrading attic insulation or sealing air leaks around windows and doors can yield substantial savings.
- Smart Thermostat Usage: Smart thermostats allow for precise temperature control and scheduling, minimizing energy waste. By optimizing heating and cooling schedules based on occupancy patterns, they can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Switching to Energy-Efficient Appliances: Investing in Energy Star-certified appliances is a practical step towards reducing energy consumption. These appliances meet stringent energy efficiency standards, leading to substantial reductions in energy use compared to older models. For instance, a refrigerator with a higher Energy Star rating will consume less electricity, lowering its carbon footprint.
Examples of Energy-Efficient Appliances
Selecting energy-efficient appliances is a critical aspect of reducing energy consumption. These appliances have a demonstrably lower environmental impact compared to traditional models.
- Energy Star Refrigerators: These refrigerators are designed to minimize energy consumption during operation. Their efficiency translates to lower electricity bills and a reduced carbon footprint. A typical Energy Star refrigerator consumes significantly less electricity compared to a standard model.
- LED Lighting: LED bulbs use far less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs. This reduction in energy consumption translates to a lower carbon footprint and cost savings. Replacing incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs is a simple yet impactful way to reduce energy usage.
- High-Efficiency Washers and Dryers: Modern high-efficiency washers and dryers are designed to use less water and energy. This translates to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. These appliances help conserve water and energy, which are essential resources.
Role of Energy Conservation in Reducing Carbon Emissions
Energy conservation plays a critical role in reducing carbon emissions. By consuming less energy, we directly lessen the demand for energy production, often from fossil fuels, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions.
Lowering energy consumption is a key component of a broader strategy to mitigate climate change.
Different Energy Sources and Their Environmental Impacts
Understanding the environmental impacts of various energy sources is crucial for making informed decisions. Different sources have varying degrees of environmental impact.
| Energy Source | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Fossil Fuels (Coal, Oil, Natural Gas) | High carbon emissions, air pollution, and contribute to climate change. |
| Nuclear Power | Low carbon emissions but potential for radioactive waste disposal. |
| Hydropower | Low carbon emissions but can have impacts on ecosystems and displace communities. |
| Solar Power | Low carbon emissions, minimal air pollution. |
| Wind Power | Low carbon emissions, minimal air pollution, potential visual impact. |
Simple Actions for Lowering Energy Use in a Home
Simple actions can significantly impact energy use within a home. Implementing these practices can result in immediate and long-term benefits.
- Unplug Electronics When Not in Use: Many electronic devices continue to consume energy even when turned off. Unplugging these devices when not in use reduces this “phantom load,” leading to lower energy consumption.
- Adjust Thermostat Settings: Raising the thermostat in winter and lowering it in summer, even by a few degrees, can significantly reduce energy usage for heating and cooling.
- Improve Ventilation: Proper ventilation can help reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling. Ensure windows and doors are sealed to prevent air leaks.
- Use Energy-Efficient Lighting: Replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with energy-efficient LED bulbs is a simple way to reduce energy consumption.
Impact of Choosing Renewable Energy Sources on Carbon Footprint Reduction
Choosing renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is crucial for reducing carbon footprints. These sources produce energy with significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Solar Panels: Solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, providing a clean and sustainable energy source. Installing solar panels directly reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers carbon emissions.
- Wind Turbines: Wind turbines harness wind energy to generate electricity. This renewable energy source helps minimize our carbon footprint and promotes a cleaner energy future.
Food Choices

Our dietary choices significantly impact our carbon footprint. From the farm to the fork, every step in the food production, processing, and transportation chain contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding these impacts allows us to make informed decisions and adopt sustainable practices to reduce our environmental impact.
The Connection Between Diet and Carbon Footprint
Food production, from growing crops to raising livestock, consumes significant resources and energy. Agricultural practices, including fertilizer use, irrigation, and land clearing, release greenhouse gases like nitrous oxide and methane. Transportation of food products over long distances, often referred to as “food miles,” further contributes to carbon emissions. The type of food consumed also plays a critical role, with some food choices having a considerably larger carbon footprint than others.
Comparison of Carbon Footprint of Different Food Types
Different food types have varying environmental impacts. Meat production, particularly from ruminant animals like cattle and sheep, generates considerably higher emissions than plant-based foods. The process of raising livestock involves significant land use, feed production, and animal waste management, all of which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Fruits and vegetables, while requiring resources for cultivation, generally have a smaller carbon footprint compared to meat products.
The specific impact of a food type also depends on factors like farming practices, transportation distances, and processing methods.
Impact of Food Miles on Carbon Emissions
Transportation plays a vital role in the carbon footprint of food. “Food miles” refer to the distance food travels from its origin to the consumer. Longer distances lead to higher emissions from transportation. Locally sourced food reduces the transportation-related carbon footprint. Supporting local farmers and producers helps minimize the environmental impact of food consumption.
Sustainable Food Choices
Making sustainable food choices can significantly reduce your carbon footprint. Prioritizing plant-based diets, including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, is a key strategy. Reducing meat consumption, particularly red meat, can substantially lower your impact. Choosing locally sourced food whenever possible minimizes transportation emissions. Supporting sustainable farming practices through purchasing certified products can also make a difference.
Consider seasonal produce for reduced transportation needs.
Environmental Impact of Various Meat Types
| Meat Type | Environmental Impact (Estimated CO2 Equivalent Emissions per kg) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Beef | >25 kg | High land use, methane emissions from rumination. |
| Lamb | >20 kg | Similar to beef, but potentially slightly lower depending on grazing practices. |
| Pork | 10-15 kg | Lower land use and methane emissions compared to beef and lamb. |
| Poultry | 5-10 kg | Generally lower impact than red meats, but still significant. |
Note: These figures are estimates and can vary based on farming practices and specific regions.
Strategies for Reducing Food Waste
Food waste is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Reducing food waste at home can make a difference. Planning meals, storing food properly, and utilizing leftovers effectively are important strategies. Supporting food banks and organizations that redistribute surplus food helps reduce waste and support communities. Learning about expiration dates and utilizing “ugly” produce can also minimize waste.
“Reducing food waste is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of our food choices.”
Waste Management

Minimizing waste generation is crucial for reducing our environmental impact. Proper waste management strategies, including recycling and composting, significantly contribute to a lower carbon footprint. Effective waste handling practices extend beyond individual actions and encompass strategies for businesses as well. By understanding the impact of our waste choices and adopting sustainable methods, we can collectively reduce our environmental burden.
Minimizing Waste Generation at Home
Effective waste reduction begins at home. By consciously modifying daily routines, individuals can dramatically lessen the amount of waste produced. This involves careful planning and intentional choices about purchasing and consumption habits.
- Reduce Consumption: Purchasing only what is needed and avoiding single-use items are essential steps. Prioritizing reusable alternatives over disposable options minimizes waste significantly.
- Proper Storage and Planning: Planning meals and shopping lists can prevent food waste. Storing food properly, utilizing leftovers creatively, and understanding expiration dates can also reduce food waste.
- Repairing and Repurposing: Instead of discarding broken items, consider repair options. Repurposing materials for new uses extends their lifespan and reduces the demand for new products.
- Choose Durable Products: Opting for durable, long-lasting products over disposable or cheaply made alternatives minimizes waste in the long run. Consider the lifecycle of a product before making a purchase.
Impact of Recycling and Composting on Carbon Footprint
Recycling and composting divert materials from landfills, thereby reducing methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. These processes also conserve natural resources, requiring less energy for the production of new materials.
- Reduced Landfill Methane: Landfills are a significant source of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Recycling and composting reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, thus minimizing methane emissions.
- Resource Conservation: Recycling and composting conserve natural resources by reducing the need to extract raw materials from the earth. This reduces the energy needed for material extraction, processing, and transportation.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Manufacturing new products from recycled materials typically requires less energy than creating products from virgin materials. This translates to lower carbon emissions.
Reusable Items to Reduce Waste
Implementing reusable items in daily life is a significant step towards waste reduction. These items replace single-use counterparts, reducing reliance on disposable materials.
- Reusable Bags: Cloth shopping bags eliminate the need for plastic bags, reducing plastic waste.
- Water Bottles: Reusable water bottles minimize the consumption of plastic water bottles.
- Food Containers: Reusable food containers can replace plastic wrap and aluminum foil, significantly reducing waste.
- Coffee Cups: Reusable coffee cups reduce the use of disposable cups, saving resources and reducing waste.
Waste Management Strategies for Businesses
Businesses can implement several strategies to manage waste effectively and reduce their environmental impact.
- Waste Audits: Conducting regular waste audits to identify areas for improvement in waste reduction and recycling efforts.
- Recycling Programs: Implementing comprehensive recycling programs that separate different waste streams and ensure proper recycling.
- Waste Reduction Strategies: Implementing strategies to reduce waste generation at the source, such as using less packaging or encouraging reusable products.
- Sustainable Procurement: Prioritizing suppliers who employ sustainable practices and minimize waste in their own operations.
Tips for Reducing Waste in Daily Life
Small, consistent changes in daily routines can significantly reduce waste generation.
- Bring Your Own: Bring reusable bags, containers, water bottles, and coffee cups when shopping, dining out, or traveling.
- Avoid Single-Use Items: Minimize the use of disposable items like plastic cutlery, straws, and plates.
- Proper Food Storage: Store food properly to prevent spoilage and extend its lifespan.
- Recycle and Compost: Properly sort and recycle and compost materials that can be reused.
Proper Waste Sorting for Effective Recycling
Effective recycling requires accurate sorting of materials. Understanding the different types of recyclable materials and their proper handling is key.
| Material | Description | Recycling Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Paper | Newspapers, magazines, cardboard | Flatten and remove any plastic or metal |
| Plastics | Bottles, containers | Check the recycling symbol for specific types |
| Glass | Bottles and jars | Rinse and remove lids |
| Metal | Cans, foil | Rinse and remove labels |
Lifestyle Changes
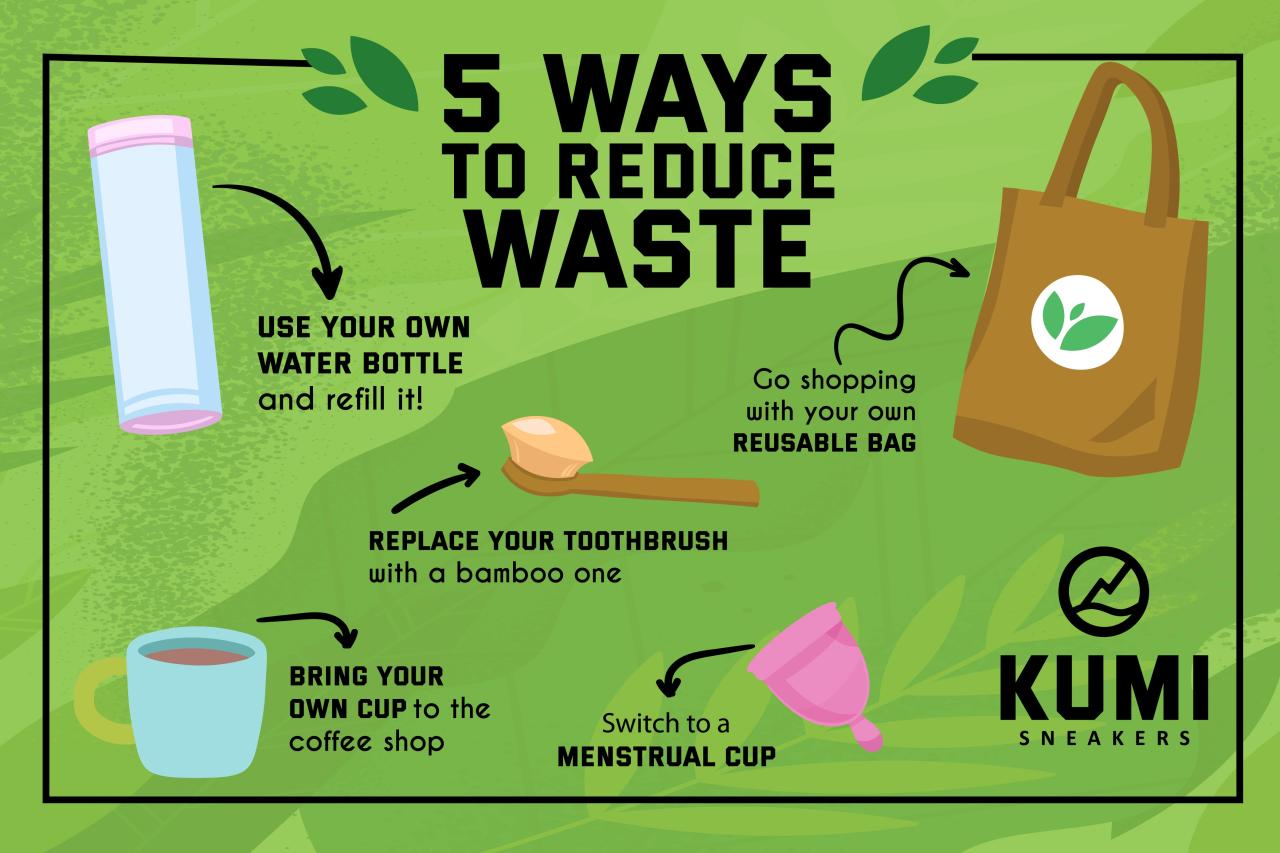
Adopting sustainable lifestyle choices is crucial for reducing your overall carbon footprint. These changes, often seemingly small, accumulate to significant environmental impact when adopted by many individuals. Incorporating eco-conscious habits into daily routines can make a substantial difference in minimizing your environmental impact.
Everyday Choices and Their Impact
Everyday choices, from the products we purchase to the energy we consume, directly influence our carbon footprint. Simple actions, such as choosing reusable alternatives to single-use plastics or opting for public transportation over personal vehicles, collectively contribute to a more sustainable future. Conscious consumerism and mindful energy use are key elements of minimizing environmental harm.
Strategies for Reducing Energy Consumption in Daily Activities
Energy conservation in daily routines is achievable through several practical strategies. Switching to energy-efficient appliances and lighting, reducing water usage, and optimizing heating and cooling systems are vital steps. Smart home technologies and mindful scheduling of energy-intensive tasks further contribute to reducing overall energy consumption.
- Using energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs reduces electricity consumption significantly.
- Implementing water-saving measures, such as low-flow showerheads and faucets, conserves water resources and reduces energy used for water heating.
- Optimizing thermostat settings and using smart thermostats allows for better control of heating and cooling needs.
- Unplugging electronics when not in use and switching to power-saving modes minimizes energy waste.
Impact of Reducing Material Consumption
Reducing material consumption is directly correlated with a decrease in carbon emissions. The production, transportation, and disposal of materials all contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Prioritizing durability and repairability over disposability, along with adopting a circular economy mindset, are critical steps towards minimizing material consumption. Minimizing packaging waste and prioritizing products with extended lifespans are vital elements.
- Buying durable, repairable products instead of disposable ones reduces the demand for new materials and decreases waste.
- Repairing and repurposing existing items extends their lifespan, reducing the need for new products.
- Prioritizing products with minimal packaging significantly decreases waste and its associated emissions.
Eco-Friendly Shopping and Consumption Habits
Sustainable shopping and consumption habits are vital for mitigating our carbon footprint. Buying secondhand, supporting local businesses, and prioritizing products with transparent supply chains are essential components of this. Choosing products with a lower environmental impact is a core aspect of this change.
- Purchasing secondhand items reduces the need for new production, lowering the associated environmental impact.
- Supporting local businesses often reduces transportation emissions associated with long-distance deliveries.
- Prioritizing products with transparent supply chains allows consumers to trace the origin and manufacturing process, ensuring sustainability.
- Choosing products with a lower environmental impact, such as those made from recycled materials, reduces waste and pollution.
Sustainable Alternatives to Conventional Products
Exploring sustainable alternatives to conventional products offers a pathway towards a more environmentally friendly lifestyle. This includes using reusable alternatives for single-use items, opting for eco-friendly cleaning products, and choosing sustainable clothing options. Shifting towards reusable products and mindful consumption habits can contribute to a more sustainable future.
- Reusable water bottles, coffee cups, and shopping bags replace single-use plastics, reducing pollution.
- Eco-friendly cleaning products often avoid harsh chemicals and harmful solvents, minimizing environmental damage.
- Sustainable clothing options, such as organic cotton and recycled materials, reduce the environmental impact of the fashion industry.
Comparing Environmental Impact of Purchasing Decisions
The environmental impact of various purchasing decisions varies significantly. A comparative analysis highlights the differences. Consider the following table illustrating the environmental impact of different product choices.
| Product Category | Conventional Option | Sustainable Alternative | Environmental Impact (estimated, relative scale) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clothing | Fast fashion synthetic fabrics | Organic cotton, recycled materials | High / Medium |
| Electronics | Single-use, non-repairable devices | Refurbished, repairable devices | Medium / Low |
| Food | Processed, imported foods | Locally sourced, seasonal produce | High / Low |
Note: Environmental impact is a relative estimate and can vary based on specific product characteristics and manufacturing processes.
Sustainable Consumption
Sustainable consumption involves making choices that minimize the environmental impact of our consumption patterns. This approach considers the entire lifecycle of products, from raw material extraction to disposal, and prioritizes resource efficiency and reduced waste generation. It is a crucial element in mitigating climate change and promoting a more equitable and environmentally sound future.Sustainable consumption is not simply about choosing “eco-friendly” products; it encompasses a broader mindset that values responsible resource use and minimizes environmental harm at every stage of the product’s existence.
This mindful approach extends beyond individual actions to influence businesses and policies towards greater sustainability.
Defining Sustainable Products and Services
Sustainable products and services are designed and produced with environmental considerations in mind. These products are often made from recycled or renewable materials, use less energy during production, and have a smaller carbon footprint throughout their lifecycle. Sustainable services, such as public transportation or renewable energy providers, also contribute to a lower environmental impact.
Considering the Entire Lifecycle of a Product
Evaluating a product’s environmental impact requires considering its entire lifecycle, from the extraction of raw materials to its eventual disposal. This lifecycle assessment (LCA) considers energy consumption, water usage, waste generation, and emissions at each stage. Understanding the complete impact allows for more informed purchasing decisions and the development of more environmentally responsible products.
The Role of Purchasing Decisions
Consumer purchasing decisions significantly impact the demand for sustainable products. By choosing products with a lower environmental impact, consumers send a clear signal to businesses that sustainable practices are valued. This can encourage businesses to adopt more sustainable manufacturing processes, supply chains, and product designs. Consumers have a direct influence on the future of sustainability.
Connection Between Sustainable Consumption and Reduced Carbon Emissions
Sustainable consumption plays a pivotal role in reducing carbon emissions. By choosing products with lower environmental impacts, consumers decrease the demand for resource-intensive production methods. This reduced demand can, in turn, incentivize businesses to invest in renewable energy sources, efficient technologies, and sustainable materials. The ripple effect of these choices contributes to a lower overall carbon footprint.
Eco-Friendly Products and Brands
Numerous eco-friendly products and brands are available in the market. These products often feature recycled materials, renewable energy sources, and sustainable packaging. Choosing such products is a practical step towards a more sustainable lifestyle.
- Recycled Materials: Products made from recycled materials, such as plastic bottles, aluminum cans, or paper, reduce the need for virgin resources and lower the environmental impact of production. Examples include clothing made from recycled plastic bottles, or furniture made from reclaimed wood.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Products using renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, in their production or operation, minimize reliance on fossil fuels and reduce carbon emissions. Examples include solar-powered calculators or computers with energy-efficient components.
- Sustainable Packaging: Products with sustainable packaging, such as compostable or biodegradable materials, reduce waste and landfill burden. Examples include food containers made from plant-based materials or products with minimal plastic packaging.
The list above presents just a few examples of eco-friendly products. Many more options exist, and consumers can easily find a wide range of sustainable choices.
Examples of brands committed to sustainable practices include Patagonia, Seventh Generation, and Interface. These companies prioritize environmentally responsible sourcing, manufacturing, and product design.
Community and Societal Impacts
Reducing our collective carbon footprint requires a shift in mindset and action, moving beyond individual choices to encompass community and societal structures. Effective strategies involve collaborative efforts, supportive policies, and a shared understanding of the importance of sustainability. Community involvement plays a crucial role in driving change and achieving ambitious emission reduction goals.
The Role of Communities in Reducing Carbon Footprints
Communities hold immense potential for fostering sustainable practices. Shared responsibility and collective action can inspire innovation and create impactful changes. Local initiatives, whether focused on energy efficiency, waste reduction, or promoting public transportation, can create tangible improvements in environmental outcomes. Local governments and community groups can organize initiatives to improve public awareness about sustainable practices.
Policies and Regulations Promoting Sustainable Practices
Government policies and regulations are instrumental in driving sustainable practices at a community level. Clear regulations, incentives, and penalties can motivate businesses and individuals to adopt environmentally friendly behaviors. Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, can incentivize emission reductions. Well-defined standards for building codes, transportation infrastructure, and energy consumption can contribute to significant environmental improvements.
Furthermore, strong policies can promote investment in renewable energy sources and sustainable infrastructure.
Examples of Successful Community Initiatives
Numerous communities worldwide have implemented successful initiatives to reduce carbon emissions. These range from community-led composting programs to the implementation of bike-sharing schemes. For instance, many municipalities have implemented programs for efficient waste management. Community gardens, encouraging local food production and reducing transportation needs, are another example of successful initiatives. Successful initiatives often involve a combination of educational outreach, public awareness campaigns, and supportive policy frameworks.
Government Policies Supporting Sustainability
Governments play a pivotal role in promoting sustainability through various policies. These policies often include incentives for renewable energy adoption, funding for energy efficiency upgrades, and support for sustainable transportation infrastructure. Many countries have introduced regulations mandating the use of energy-efficient appliances and building standards. For example, building codes requiring energy-efficient insulation and windows are prevalent in many jurisdictions.
Impact of Collective Action on Emission Reduction Goals
Collective action, when well-organized and implemented, can significantly contribute to achieving emission reduction goals. Community-wide initiatives can inspire wider adoption of sustainable practices. Public awareness campaigns, community workshops, and shared resources can motivate individuals and businesses to make sustainable choices. Collaboration among individuals, businesses, and governments can amplify the impact of individual actions. For example, community-wide energy efficiency programs, combined with incentives for renewable energy adoption, can yield significant emissions reductions.
Comparison of Community-Level Initiatives
| Initiative | Description | Impact | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community Composting | Residents collect and compost organic waste | Reduces landfill waste, creates nutrient-rich soil | Requires education and infrastructure (composting facilities) |
| Bike-sharing Programs | Provides readily available bikes for commuting | Reduces reliance on cars, promotes physical activity | Requires adequate infrastructure (bike lanes, parking) |
| Local Food Systems | Supporting local farms and markets | Reduces transportation emissions associated with food | Requires coordination between producers and consumers |
| Energy Efficiency Programs | Promoting energy-efficient practices and upgrades | Reduces energy consumption and associated emissions | Potential upfront costs for upgrades |
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, reducing your carbon footprint is a journey, not a destination. By combining individual actions with community-level initiatives and embracing sustainable consumption, we can collectively work towards a more environmentally responsible future. This guide has presented a roadmap for making conscious choices, ultimately contributing to a healthier planet for generations to come.